1.自定义启动器
hello-spring-boot-starter(启动器)
hello-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure(自动配置包)
1.1 创建一个空项目
1.2 在空项目的基础上,添加maven空项目,项目名称叫做
hello-spring-boot-starter
再添加一个springboot空项目,项目名称hello-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure
1.3 hello-spring-boot-starter(启动器)的pom.xml文件中,将hello-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure的groupId和artifactId作为依赖添加进去
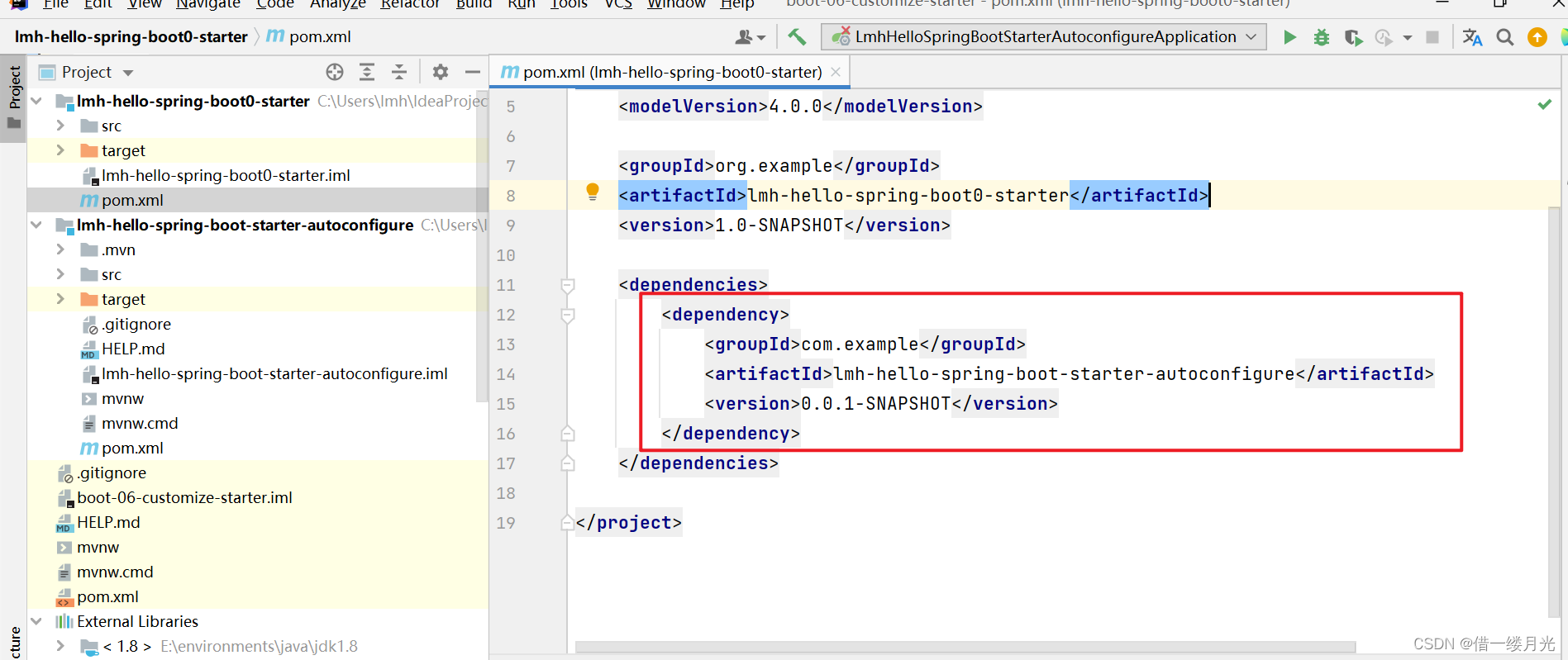
1.4 注意每个类所在路径
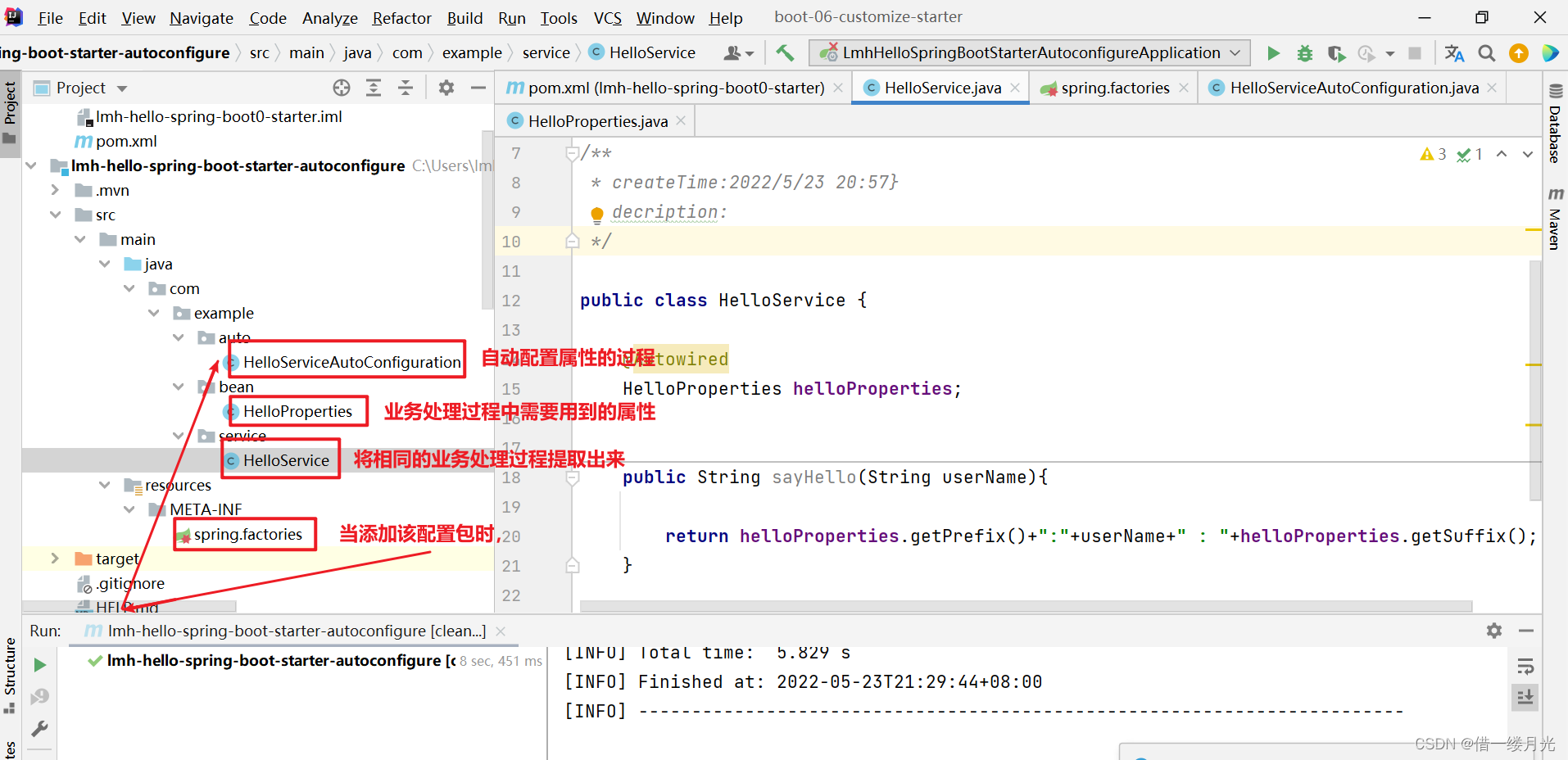
创建HelloService类,业务处理的过程
public class HelloService {
@Autowired
HelloProperties helloProperties;
/*
* param:用户名
* decription:再用户名前后 加入前后缀
* */
public String sayHello(String userName){
return helloProperties.getPrefix()+":"+userName+" : "+helloProperties.getSuffix();
}
创建HelloProperties类
@ConfigurationProperties("bigworldxld.hello") //可用于便捷配置属性值
public class HelloProperties {
private String prefix="隐隐";
private String suffix="星星";
public String getPrefix() {
return prefix;
}
public void setPrefix(String prefix) {
this.prefix = prefix;
}
public String getSuffix() {
return suffix;
}
public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
this.suffix = suffix;
}
}
创建HelloServiceAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class) // 默认放在容器中
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "bigworldxld.hello", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)//条件是有这个属性才生效
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HelloService.class) //当容器中没有HelloService组件时,下面才生效
public HelloService helloService(){
HelloService helloService = new HelloService();
return helloService;
}
}
在resources文件夹下面新建一个META-INF文件,并在下面创建spring.factories文件。Auto configure 启动时,就开始加载 HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.example.auto.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
1.5 将启动器和配置包 先clean,再install添加到maven仓库中
1.6 使用在新项目中,添加启动器的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>hello-spring-boot0-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
application.properties中
bigworldxld.hello.prefix=username
bigworldxld.hello.suffix=77777
创建HelloController类
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(){
String s = helloService.sayHello("李白");
return s;
}
}
1.7 地址访问
localhost:8080/hello
2.starter启动原理
pom.xml 添加starter,引入autoConfigure包
starter—> autoConfigure—>spring-boot-starter
autoconfigure包中配置使用META-INF/spring.factories 中EnableAutoConfiguration的值,使项目启动加载指定的自动配置类
编写自动配置类 xxxAutoConfiguration –> xxxProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(“bigworldxld.hello”)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HelloService.class) //当容器中没有HelloService组件时,下面才生效
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class) // 默认放在容器中
@Bean 组件
引入starter — xxxAutoConfiguration — 容器中放入组件 —- 绑定xxxProperties —- 配置项
参数尽量设置默认值,这也是springboot核心思想,约定大于配置。比如有一个变量,需要根据实际情况,确定参数设置成什么值最好,让别人尽量可以不配置
一个参数就可以使用这个starter模块,而当别人发现默认的配置无法满足自己要求的时候,自己又可以进行设置。比如有一个参数pageSize,默认设置成100,
如果用户配置了,会默认覆盖,不用做任何逻辑。我们先做 int pageSize = 100,使用者后做pageSize=50,所以是可以覆盖的。如果是整型,不设置初始化都无法使用,难道非要用户设置一个值,程序才可以运行吗,这就违背了springboot的初衷。